Narrow-Line Seyfert 1: Astronomers have discovered a new active galaxy – the Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 (NLS1) galaxy- identified as the farthest gamma-ray emitting galaxy that has so far been stumbled upon.
Analysis
- Ever since 1929, when Edwin Hubble discovered that the Universe is expanding, it has been known that most other galaxies are moving away from us.
- Light from these galaxies is shifted to longer (and this means redder) wavelengths – in other words, it is red-shifted.
- Scientists have been trying to trace such red-shifted galaxies to understand the early Universe.
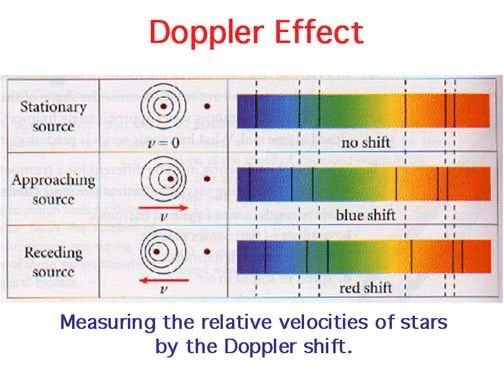
- To be accurate, the red shifts observed in distant objects are not exactly due to the Doppler phenomenon, but are rather a result of the expansion of the Universe.
- Doppler shifts arise from the relative motion of source and observer through space, whereas astronomical redshifts are ‘expansion redshifts’ due to the expansion of space itself.
- Two objects can actually be stationary in space and still experience a red shift if the intervening space itself is expanding.
- The terms redshift and blueshift apply to any part of the electromagnetic spectrum, including radio waves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays.
Notable uses of redshift
- Redshift helps astronomers compare the distances of faraway objects.
- Scientists can use redshift to measure how the universe is structured on a large scale.
- The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is an ongoing redshift project that is trying to measure the redshifts of several million objects.
What can gamma rays tell us about the cosmos?
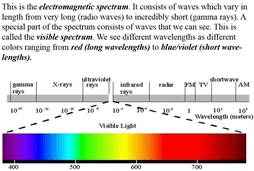
- Gamma-rays are the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, with over 10,000 times more energy than visible light photons.
- Gamma-rays coming from space are mostly absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere.
- So, gamma-ray astronomy could not develop until it was possible to get our detectors above all or most of the atmosphere, using balloons or spacecraft.
- Gamma-ray astronomy presents unique opportunities to explore the solar flares, supernovae, neutron stars, black holes, and active galaxies.
Do you know?
- Something similar happens to sound waves when a source of sound moves relative to an observer. This effect is called the ‘Doppler effect.’
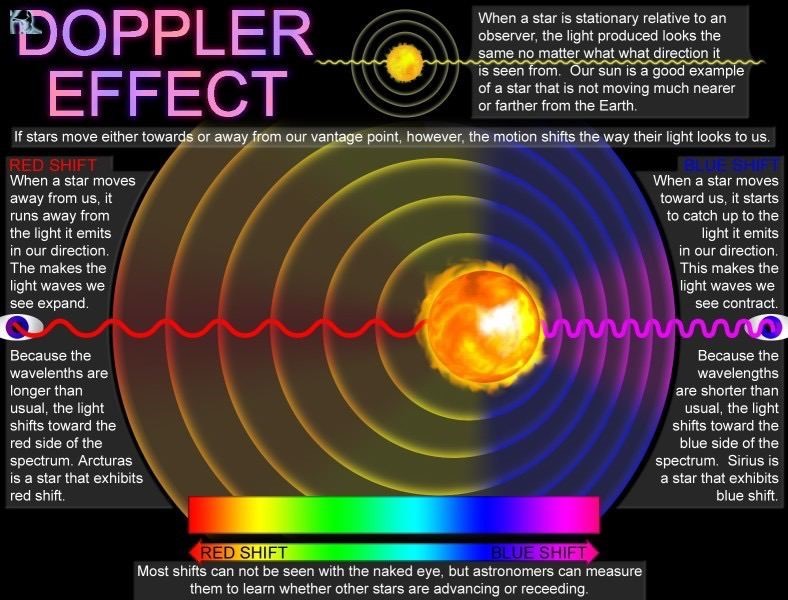
- If the two are approaching, then the frequency heard by the observer is higher; if they move away from each other, the frequency heard is lower.
- There are many everyday examples of the Doppler effect – the changing pitch of police and ambulance sirens, or train whistles and racing car engines as they pass by. In every case, there is an audible change in pitch as the source approaches and then passes an observer.