UPSC PRELIMS+MAINS
Science and Technology/Defence/Space
-
Major Initiatives in the Defence Sector (PIB)
- iDEX4Fauji is a first of its kind initiative, launched to support innovations identified by members of the Indian Armed Forces to bolster frugal innovation ideas from soldiers/ field formations.
- iDEX4Fauji would open this window and allow our Faujis to become part of the innovation process and get recognised and rewarded.
- In order to further strengthen our defence system and make it self- reliant the participation of private sector is also crucial.
- For this the Ministry of Defence has taken certain steps like:
- partnerships with private sector,
- technology transfer,
- 74 % FDI through automatic route and
- the recently released negative list of 101 items for import ban after a stipulated period.”
- Under Defence India Startup Challenge (DISC) 4, eleven challenges from Armed Services/ DPSUs/ OFB were thrown open to prospective startups, innovators, MSMEs alike to provide their innovative ideas on technologies which find their application in the defence sector.
- The iDEX initiative of the Department of Defence Production was launched in 2018 with the objective to encourage and nurture start-ups in the Indian Defence sector and create an ecosystem where Start-ups, MSMEs and individual innovators could interact easily with the Indian defence establishment and provide the latest technological innovations for specific challenges experienced in operational environments through co-development and co-production of innovative solutions.
- The aim was to fund 250 start-ups and achieve 50 tangible innovations in the next five years.
- The iDEX would be funded and managed by the Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO), formed as a not for profit company with nominal capital by Public Sector Undertakings Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- Start-ups/ individuals to receive innovation grants in technological areas through the Prototype funding guidelines called “Support for Prototype and Research Kickstart” (SPARK), which entail provisioning of grants upto Rs 1.5 crore to the Startups on the basis of milestones through multiple tranches, for prototype development.
- Ministry of Defence has also set up the ‘Technology Development Fund (TDF)’ which aims at funding the development of defence and dual-use technologies that are currently not available with the Indian defence industry or have not been developed so far.
- The funding is to public and private sector industry especially micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) that may work in collaboration with the academia or research institutions to carry out innovation, research and development.
- TDF also aims at encouraging participation of public/private industries through the provision of grants, so as to create an ecosystem for enhancing cutting edge technology capability for defence applications.
-
BrahMos Missile Featuring Indigenous Booster Successfully Flight Tested (PIB)
- BrahMos surface-to-surface supersonic cruise missile featuring indigenous Booster and Airframe Section along with many other ‘Made in India’ sub-systems was successfully flight tested for designated range.
- It is one more major step in enhancing the indigenous content.
- The BrahMos land-attack Cruise Missile (LACM) was cruising at a top speed of Mach 2.8.
- Today’s successful launch has paved the way for the serial production of the indigenous booster and other indigenous components of the powerful BrahMos Weapon System realising Atmanirbhar Bharat pledge.
BrahMos:
- The name BrahMos is formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia.
- It was developed as a joint venture between India and Russia.
- BrahMos is a two-stage supersonic (denoting a speed greater than that of sound) cruise missile that is first test-fired in June, 2001.
- It has been demonstrated in various configurations in land-attack, anti-ship and from the air.
- The Army and the Navy have already inducted the missile, while the air-launched variant is undergoing trials.
- It has a strike range of around 290 km and is described as the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile.
- It is a two stage missile with a solid propellant booster engine as its first stage which brings it to supersonic speed and then gets separated.
- The liquid ramjet or the second stage then takes the missile closer to 3 Mach speed in cruise phase.
- It carries a conventional warhead weighing 200 to 300 kgs.
- It is the first supersonic cruise missile known to be in service.
Special Features:
- Universal for multiple platforms
- Fire and forget the principle of operation
- High supersonic speed all through the flight
- Long flight range with varieties of flight trajectories
- Low radar signature
- Shorter flight times leading to lower target dispersion and quicker engagement
- Pin point accuracy with high lethal power aided by large kinetic energy on impact
- Stealth technology and guidance system with advanced software
- Non-interception with any known system in the world
-
CSIR Technologies for rural development (PIB)
- Context: CSIR Technologies for rural development launched under a joint initiative of Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), Unnat Bharat Abhiyan (UBA), Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IITD) and Vijnana Bharti (VIBHA).
- The technologies released included:
- Improved bee hive for quality and hygienic extraction of honey
- Technology for manufacturing of Ginger paste
- Dehumidified drier for food and agri products
- Technology for agricultural waste (wheat bran, sugarcane bagasse and fruit peels) based biodegradable plates, cups and cutleries
- Sharing this article to make candidates understand depth of rural agricultural oppurtunities that can be commercialized. Use this to enrich your Answers.
Analysis
- “Unnat Bharat Abhiyan” is a flagship programme of Ministry of Education conceptualised and launched in IIT Delhi, with a vision of transformational change in rural development processes by leveraging knowledge institutions to help build the architecture of an Inclusive India.
- Vijnana Bharti(Vibha): VIBHA, a science movement with swadeshi
- SwadeshiScience Movement was started in Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru by some eminent scientists under the guidance of Prof. K. I. Vasu.
- One of the founding principles of VIBHA is – SwadeshiMovement with modern sciences adapted to national needs.
B) Geography, Environment and Biodiversity
4.Eco-sensitive zones (ESZs) and Western Ghats (IE)
- Context: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has expressed concern after six states asked the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change to whittle down the size of the eco-sensitive zone (ESZ) under the ecologically fragile Western Ghats by 6,386.65 sq km.
Analysis
- The Western Ghats cover six states — Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- The K Kasturirangan Committee had in 2012 earmarked around 60,000 sq km as ESZ.
- In 2014, the then MoEF issued a draft notification declaring 56,825 sq km in the Western Ghats as ESZ.
- The notification has been hanging fire for more than a decade, as many states and the Centre believe that once areas under the Ghats are classified as ESZ, development activities will be off-limits.
- The ministry said some states are concerned that two committee reports (Gadgil Commission and K Kasturirangan Committee) on the delineation of the Western Ghats were based on the 2001 census.
- Ecologically Sensitive Areas (ESAs) have been identified and notified by the Indian Ministry of Environment & Forests (MoEF) since 1989.
- Notifications declaring areas as ESAs are issued under the Environment (Protection) Act 1986.
- However, the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 does not mention the word “Eco-Sensitive Zones”.
-
Southwest monsoon (TH, pg 10)
- Context: The southwest monsoon this year has ended with an 8.7% surplus, surpassing estimates by the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- This is also the first time since 2010 that India has got more than 100% of its long period average (LPA) of 88 cm in consecutive years.
- Last year, India saw record rainfall of 110% of the LPA, the highest in a quarter century.
- India has never got over 105% of the LPA in consecutive years in at least 30 years, according to records available since 1988 on the IMD website.
- A developing La Nina, the converse of an El Nino, which is a heating of the central equatorial Pacific and responsible for diminished monsoon rain over India, too, contributed to munificent rain this year.
- The IMD, in its forecasts, had anticipated ‘normal’ rain, defined as 96-104% of the LPA. Rains above 110% LPA are termed ‘excess’ and this year has fallen only a tad short.
- El Nino
- El Niño is an abnormal warming of water in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean every three to five years and can last up to 18 months.
- Climate records of El Niño go back millions of years, with evidence of the cycle found in ice cores, deep sea muds, coral, caves and tree rings.
What causes an El Niño?
- Scientists do not yet understand in detail what triggers an El Niño cycle.
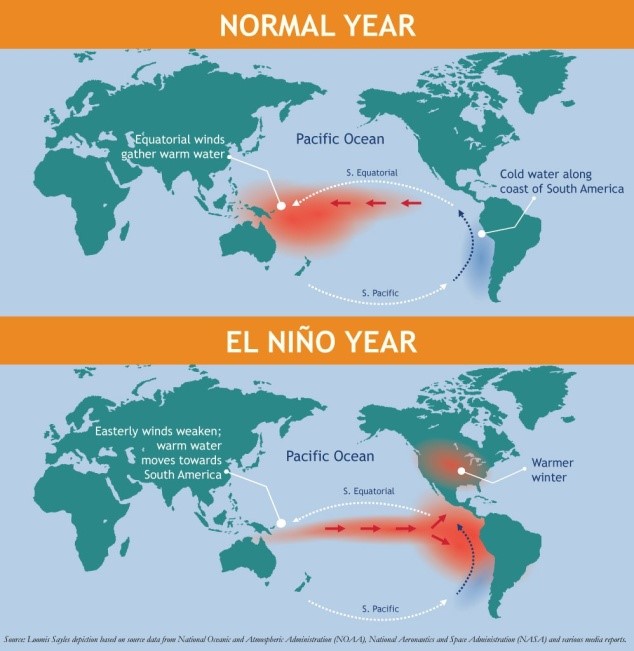
- Normally, due to the presence of cold Peru Current (Humbolt Current) along the coast of Peru (South America), there is high-pressure area in the eastern Pacific Ocean along the Peru Coast.
- Therefore, air moves from the eastern Pacific Ocean to the western Pacific Ocean where there is comparatively a low pressure.
- Because of the warmer oceans, this air gets lots of moisture due to evaporation on the way.
- This warm moist air rises to high levels of the atmosphere in the western part of the Pacific Ocean and causes rainfall in Indonesia, eastern and northern Australia etc.
- The rise of warm air finally results in its cooling in the upper atmosphere. A part of this air moves towards the eastern Pacific Ocean in the upper atmosphere and descends over the eastern Pacific Ocean and helps to sustain the higher pressure there and again moves towards the western Pacific Ocean.
- This way we have a complete circulation of air between eastern and western Pacific Ocean. This circulation is called Walker Circulation.
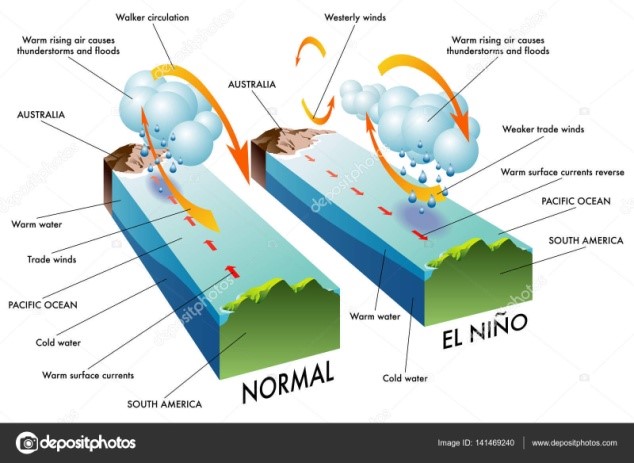
- During El Nino years, due the abnormal warming of water in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean the high-pressure area in the eastern Pacific Ocean weakens, thus the wind moving towards the east (called easterly wind) weakens or even reverses its direction.
- Thus, there is less rainfall/drought in the western Pacific Ocean (Indonesia, eastern and northern Australia and nearby areas including India etc.) whereas due to the presence of warm water in the eastern Pacific Ocean near Peru cloud formation takes place which causes heavy rainfall/floods in the coastal Peru.
- The atmospheric pressure in the eastern Pacific Ocean is measured at a place called Tahiti whereas the atmospheric pressure in the western Pacific Ocean is measured at a place called Darwin.
- During normal years there is high pressure at Tahiti and low pressure at Darwin. This situation exactly reverses during El Nino years and this phenomenon is called Southern Oscillation.
- There is also an opposite of an El Niño, called La Niña.
- This refers to times when waters of the tropical eastern Pacific are colder than normal and trade winds blow more strongly than usual.
- El Nino and Southern Oscillation together sometimes called
- Typically, El Niños occur more frequently than La Niñas.
El Nino and Indian Monsoon:
- An analysis of rainfall records of the past 132 years has revealed that severe droughts in the country have always been accompanied by El Nino events, but not all such weather conditions have led to the failure of monsoons.
- The El Nino events in 1965, 1972, 1982 and 1987 were bad for India but the 1997 El Nino, despite being the strongest in the century, did not affect monsoons (Thus strong El Niño events are not always associated with drought).
- This led many experts to conclude that the link between monsoons and global weather event was wearing off. But the India Meteorological Department still takes into account El Nino for forecasts.
- Researchers also believe that even the location of the warming in the Pacific may possibly have an influence on the monsoon. Anomalous warming in the Central and East Pacific (Nino 3.4 region) could have a more profound adverse impact on the monsoon than when the warming shifts to the adjoining far east Pacific (Nino 3. region).
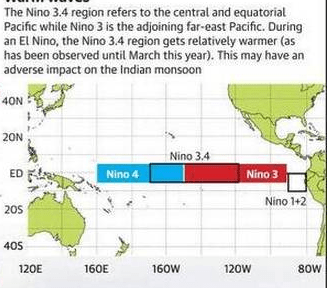
- What’s worth noting is that El Niño is impacting the Indian monsoon more than before. Since 1991, six of the nine times that El Niño occurred, the Indian monsoon was affected. Mathematically, that’s tantamount to an impact probability of over 65%.
- A closer look also reveals two interesting developments: One, the frequency of El Niño has increased—it has occurred six times since 2000. Two, Indian monsoons suffered in all but one of these years, taking the probability of impact to over 80% in recent times.
Mechanism:
- As discussed above, rise and cooling of the warm moist air in the atmosphere in the western part of the Pacific Ocean in the upper atmosphere results in its division into at least two parts.
- A part of this air moves towards the eastern Pacific Ocean in the upper atmosphere and descends over the eastern Pacific Ocean and helps to sustain the higher pressure there.
- One part also descends near East Africa and aids the formation of the Mascarene High-Pressure zone. This increases the difference between the HP in the south over the Mascarene High-Pressure zone and the LP in the Indian subcontinent. Thus more moisture-laden winds move towards the Indian Subcontinent.
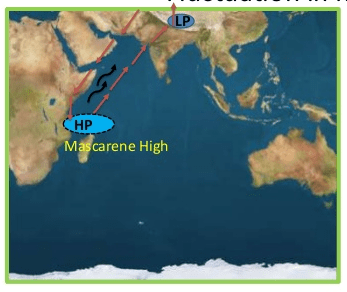
- During El Nino years, due the abnormal warming of water in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean the high-pressure area in the eastern Pacific Ocean weakens, thus the wind moving towards the east (called easterly wind) weakens or even reverses its direction. Thus, less or no air descends near East Africa which results in the weakening of the Mascarene High-Pressure zone.
Other effects of El Niño:
- During an El Niño, the Pacific’s warmest surface waters occurs offshore of northwestern South America (as El Nino begins when warm water in the western tropical Pacific Ocean shifts eastward along the equator toward the coast of South America. Normally, this warm water pools near Indonesia and the Philippines).
- Prevailing easterly trade winds weaken and even reverse direction during the El Niño climate phenomenon.
- The location of tropical storms shifts eastward during an El Niño because atmospheric moisture is fuel for thunderstorms, and the greatest amount of evaporation takes place above the ocean’s warmest water.
- Record rainfall often strikes Peru, Chile and Ecuador during an El Niño year.
- Fish catches offshore South America are typically lower than normal as during El Niño years, warm water persists and deepens, and cold, upwelling, nutrient rich water (which is present during normal years) fails to reach surface and the marine life migrates north and south, following colder water.
- Strong El Niños are also associated with above-average precipitation in the southern tier of the United States from California to the Atlantic coast.
- Indonesia and northeastern South America tend toward drier-than-normal conditions.
- Temperatures in Australia and Southeast Asia run hotter than average.
- El Niño-caused drought can be widespread, affecting southern Africa, India, Southeast Asia, Australia, the Pacific Islands and the Canadian prairies.
- In general, warm El Niño events are characterized by more tropical storms and hurricanes in the eastern Pacific and a decrease in the Atlantic, Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
- An El Niño creates stronger wind-shear and more-stable air over the Atlantic, which makes it harder for hurricanes to form.
- However, the warmer-than-average ocean temperatures boost eastern Pacific hurricanes, contributing to more-active tropical storm seasons.
- Wind shear is defined as the amount of change in the wind’s direction or speed with increasing altitude
C) Economy
6.RBI extends WMA limit and OD (overdraft) relaxations for six months (TH)
- Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has decided to extend the interim relaxation in WMA (Ways and Means Advances) limits and OD (overdraft) regulations for States/ Union Territories (UTs) for another six months till March 31, 2021.
Analysis
- Both these relaxations, which are aimed at helping States/UTs overcome short-term liquidity mismatches, are currently available till September 30, 2020.
- Under WMA, States/ UTs get short-term credit up to three months from the RBI to bridge temporary mismatches in cash flows.
- In April, the RBI had announced an increase in WMA limit of the States/UTs by 60 per cent over and above the level as on March 31, 2020.
- This was done to provide greater comfort to them for undertaking Covid-19 containment and mitigation measures and to enable them to plan their market borrowings.
- Further, in order to provide flexibility to State governments to tide over their cash flow mismatches, the OD regulations were relaxed with effect from April 7.
- Under the OD relaxation, the number of days for which a State/ UT can be in overdraft continuously was increased to 21 working days from 14 working days; and the number of days for which a State/ UT can be in overdraft in a quarter was increased to 50 working days from 36 working days.
- The interest rate on WMA is the Repo rate (4 per cent).
- For OD up to 100 per cent of WMA limit, the interest rate is 2 per cent above the Repo rate. For OD exceeding 100 per cent of the WMA limit, the interest rate is 5 per cent above the Repo rate.
-
Index of Eight Core Industries (PIB)
- Context: The Office of Economic Adviser, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade is releasing Index of Eight Core Industries for the Month of August, 2020.
Analysis
Core Industries
- Index of Eight Core Industries has the base: 2011-12.
- The Eight Core Industries comprise 27 % of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The data relating to core industries is released by the Office of the Economic Adviser, Department for Promotion of Industry & Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The Index of Eight Core Industries is a monthly production index, which is also considered as a lead indicator of the monthly industrial performance.
- Since April, 2014, Electricity generation data from Renewable sources are also included.
- Since March 2019, a new steel product called Hot Rolled Pickled and Oiled (HRPO) under the item ‘Cold Rolled (CR) coils’ within the production of finished steel has also been included.
- The eight core industries are, in descending order of their weights:
- Petroleum Refinery Products (weight: 28.04%)
- Electricity (weight: 19.85%)
- Steel (weight: 17.92 %)
- Coal production (weight: 10.33 %)
- Crude Oil (weight: 8.98 %)
- Natural Gas (weight: 6.88 %)
- Cement (weight: 5.37%)
- Fertilizer (weight: 2.63 %)
The aluminium sector as India’s ninth core industry
- The Centre must actively consider classifying the aluminium sector as India’s ninth core industry, according to a report by VK Saraswat, NITI Aayog member, and Aniruddha Ghosh, a Delhi-based economist.
- The aluminium sector contributes to nearly 2 per cent of manufacturing GDP and is a high direct and indirect employment multiplier creating close to 800,000 jobs.
Aluminium
- Aluminium is one of the Earth’s most abundant metals and is produced from cryolite and bauxite mining.
- This is because the two minerals are large sources of Aluminium; bauxite is processed to create alumina, which is then refined to create Aluminium.
- Aluminium is one of the most in-demand industrial metals because it is extremely versatile.
- The silvery metal is non-toxic and lightweight, perfect for making food and beverage cans; it also has a high thermal conductivity, is corrosion resistant and can be easily cast, machined and formed.
- Because the metal is a good electrical conductor and is less costly than copper and other more expensive metals, it is often used in electricity transmission lines.
- It is also the second most malleable metal and sixth most ductile. It is non-magnetic and non-sparking.
- While Aluminium has many benefits, strength is not one.
- Due to this, Aluminium is often used as an alloy in steel manufacturing, mixing with stronger, less adaptable metals like copper, manganese, magnesium and silicon.
- One last benefit of Aluminium is its high recovery rate.
- Because Aluminium can be recycled time and time again, it has as much as 95 percent energy savings compared to primary production costs.
- The eight top Aluminium-producing countries are:
- China (responsible for almost half of global Aluminium output), Russia, India, Canada, United Arab Emirates, Australia, Norway and United States.
Office of the Economic Adviser (OEA)
- It is an attached office of the Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
The main statistical functions of the Office of Economic Adviser include, inter alia the following:
- Compiling and releasing monthly Wholesale Price Indices
- Compiling and releasing monthly Index of Core Industries Production
- Developing other Indices on experimental basis, e.g. select business service price indices
- Supervising as a ‘source agency’
- Monthly Statistical compilation of macro indicators
-
External Debt of India (TH, pg 14)
- Context: The June 2020 external debt level was lower by $3.9 billion over its level of $558.4 billion at end-March 2020, the RBI said.
- As per the standard practice, India’s external debt statistics for the quarters ending March and June are released by the Reserve Bank of India with a lag of one quarter and those for the quarters ending September and December by the Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
Analysis
- At end-June 2020, India’s external debt was placed at US$ 554.5 billion, recording a decrease of US$ 3.9 billion over its level at end-March 2020.
- However, the external debt to GDP ratio increased to 21.8 per cent at end-June 2020 from 20.6 per cent at end-March 2020. (This means despite external debt decrease there was significant fall in GDP numbers, thereby increasing this ratio)
- Commercial borrowings remained the largest component of external debt, with a share of 38.1 per cent, followed by non-resident deposits (23.9 per cent) and short-term trade credit (18.2 per cent).
- US dollar-denominated debt remained the largest component of India’s external debt, with a share of 53.9 per cent at end-June 2020, followed by the Indian rupee (31.6 per cent), yen (5.7 per cent), SDR (4.5 per cent) and the euro (3.5 per cent).
- The borrower-wise classification shows that the outstanding debt of both government and non-government sectors decreased at end-June 2020.
- Components of External Debt in India as per RBI:
- 1. Multilateral
- 2. Bilateral
- 3. IMF
- 4. Trade Credit
- 5.Commercial Borrowings
- 6. NRI Deposits
- 7. Rupee Debt
- 8. Short-term Debt
- Commercial borrowings are inclusive of trade credit, FPI investments in corporate debt instruments and a portion of non-government multilateral and bilateral borrowings.
D) Indices/Committees/Reports/Organisations
8)“Crime in India” 2019 Report (IE)
- Context: The annual National Crime Record Bureau’s “Crime in India” 2019 report has been released.
Analysis
- From 2018, the rate of crime against women has risen by 7.3%.
- UP had most cases of violence against women in 2019.
- Assam reported the highest rate of crimes against women per lakh population.
- Majority of these cases under the Indian Penal Code were registered under ‘cruelty by husband or his relatives’ (30.9%) followed by ‘Assault on women with intent to outrage her modesty’ (21.8%), ‘kidnapping and abduction of women’ (17.9%).
- Crime against Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) saw an increase of over 7% and 26% respectively in year 2019 compared to 2018.
- The crime bureau data also showed a significant rise in cases of crimes against children.
- From 2018, crimes against children have gone up by 4.5% in 2019.
- Of these, about 46.6% were cases of kidnapping and 35.3% cases were related to sexual offences.
- Uttar Pradesh also had the highest number of crimes against girl children under the POCSO Act, followed by Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
- Murder and kidnapping cases across India in 2019 reported a slight dip from the previous year.
- “Dispute” was the motive in most murder cases followed by “personal vendetta or enmity.’’
- Cybercrimes increased by 63.5% in 2019.
- In 2019, 60.4% of cybercrime cases registered were for the motive of fraud, followed by sexual exploitation, with 5.1%, and causing disrepute with 4.2%.
National Crime Records Bureau
- NCRB, now under the Home Ministry, was set-up in 1986 to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- NCRB developed Crime Criminal Information System (CCIS) in the year 1995, Common Integrated Police Application (CIPA) in 2004, and finally Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & System (CCTNS) in 2009.
- National Digital Police Portal allows search for a criminal/suspect on a national data base apart from providing various services to citizens like filing of complaints online and seeking antecedent verification of tenants, domestic helps, drivers etc.
- NCRB also compiles and publishes annual National Crime Statistics e., Crime in India, Accidental Deaths & Suicides, Prison Statistics and Finger Prints.
- NCRB has been conferred with “Digital India Awards 2016-Silver Open Data Championship” from the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- NCRB has also floated various IT based Public Services like, Vahan Samanvay (online Motor Vehicle Matching), Talash (matching of missing persons and dead bodies).
- In addition, NCRB also maintains Counterfeit Currency Information and Management System (FICN) and Firearms Coordination System for lost and recovered firearms.
Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children (CCPWC) portal
- Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has launched Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children (CCPWC) portal to check objectionable online content.
- The portal will allow citizens to lodge complaints on objectionable online content related to child pornography, child sexual abuse material and sexually explicit material such as rape and gang rape.
- The portal will enable citizens to report complainants in without disclosing their identity.
- It also allows complainants to upload objectionable content and URL to assist in investigation by state Police.
- The complaints registered through this portal will be handled by police authorities of respective State/UTs.
- In this regard, NCRB has been notified as Central Government nodal agency to issue notices under the Information Technology (IT) Act.
Other functions of NCRB
- To function as a clearinghouse of information on crime and criminals including those operating at National and International levels so as to assists the investigators.
- To store, coordinate and disseminate information on inter-state and international criminals from and to respective States, national investigating agencies, courts and prosecutors in India without having to refer to the Police Station records.
- To collect and process crime statistics at the National level.
- Executive and develop computer-based systems for the Central Police Organisations.
- To function as the National storehouse of fingerprint (FP) records of convicted persons including FP records of foreign criminals.
-
Amnesty International halts India operations (TH)
- Context: Amnesty International has been forced to shut down operations in India and lay off all staff after the Indian government froze its bank accounts.
- The Indian enforcement directorate, an agency that investigates economic crimes, froze the accounts of Amnesty’s Indian arm this month after the group published two reports highly critical of the government’s human rights record.
Amnesty International (AI)
- Amnesty International (AI) is an international nongovernmental organization (NGO) founded in London in 1961.
- It seeks to publicize violations by governments and other entities of rights recognized in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), especially freedom of speech and of conscience and the right against torture.
- It actively seeks the release of political prisoners and the relief, when necessary, of their families.
- It also works with intergovernmental human rights bodies to expand and enforce human rights protections in international law.
- It also promotes abolishing the death penalty to protecting sexual and reproductive rights, and from combating discrimination to defending refugees and migrants’ rights.
- In 1977 AI was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace.
- Its logo is a burning candle wrapped in barbed wire. Headquarters are in London.
Human Rights Day
- It is observed by the international community every year on 10 December.
- It commemorates the day in 1948 the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- The Declaration with its broad range of political, civil, social, cultural and economic rights is not a binding document.
Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action
- Also known as VDPA, it is a human rights declaration adopted by consensus at the World Conference on Human Rights in June 1993 in Vienna, Austria.
- The position of United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights was recommended by this Declaration and subsequently created by the General Assembly.
What are human rights?
- Human rights are the basic rights and freedoms that belong to every person in the world, from birth until death.
- They can never be taken away, although they can sometimes be restricted – for example, if a person breaks the law, or in the interests of national security.
- These basic rights are based on shared values like dignity, fairness, equality, respect and independence.
- These values are generally defined and protected by law.
Paris Principles
- The Paris Principles are a set of international standards which frame and guide the work of National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs). They were adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1993.
Directorate of Enforcement
- Directorate of Enforcement is a specialized financial investigation agency under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance (Department of Investment and Public Asset Management; Expenditure; Revenue; Financial Services; Economic Affairs are other departments of the Ministry).
- It enforces the following laws: –
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) – A Civil Law.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) – A Criminal Law.
-
E) Miscellaneous
-
11 )India and the Netherlands (PIB)
- NITI Aayog and Embassy of the Netherlands, New Delhi, signed a Statement of Intent (SoI) on to support the decarbonization and energy transition agenda for accommodating cleaner and more energy.
- The Netherlands and India share a long history of trade and investment.
- It is India’s sixth-largest EU trading partner—as much as 20% of India’s exports to the European continent goes through the Netherlands, making it India’s ‘gateway to Europe’—and one of the top five investors in the country.
- It is also the third-largest source of Foreign Direct Investment for India.
-
Rythu Bharosa Kendralu (RBK) (PIB)
- Under an initiative of home delivery of Fertilizers in Andhra Pradesh through Rythu Bharosa Kendralu (RBK) state Government has launched 10,641 Rythu Bharosa Kendralu (RBKs) in all gram panchayats to provide farmers with quality inputs and allied services.
- Under this system, farmers after biometric authentication can order fertilizers from RBK (Rythu Bharosa Kendra) in their village and fertilizer will be delivered at their doorstep.
Source-The Hindu, PIB, IE and Others