Money Laundering for UPSC
Money Laundering for UPSC refers to the conversion or “Laundering” of money which is illegally obtained, so as to make it appear to originate from a legitimate source.
INDEX
- Basics of Money Laundering
- Process of Money Laundering
- Vulnerability of India
- Why it still persists
- Adverse consequences
- GOI Steps & Laws
- Global Efforts
- Previous Year Questions
- PMLA Amendment 2018
Money Laundering Definition
- Money Laundering refers to the conversion or “Laundering” of money which is illegally obtained, so as to make it appear to originate from a legitimate source.
Examples of Money Laundering
- Illegal arms sales,
- smuggling, and the
- activities of organized crime, including for example drug trafficking and prostitution rings.
- Embezzlement,
- insider trading,
- bribery and
- computer fraud schemes
Two Myths on money laundering
Myth 1: Converting black money into white is money laundering.
Reality: If the launderer simply conceals income and violates I-T Act, he will not necessarily be booked for money laundering. He or she can be booked only if one of the 30 acts (statutes) which are included in the Prevention of Money Laundering Act is violated.
Myth 2: Money launderers indulge in big-ticket scams.
Reality: If someone makes a gain of Rs 30 lakh or above by violating any of the 24 acts, like the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, SEBI Act, Prevention of Corruption Act, it will be considered a case of money laundering.
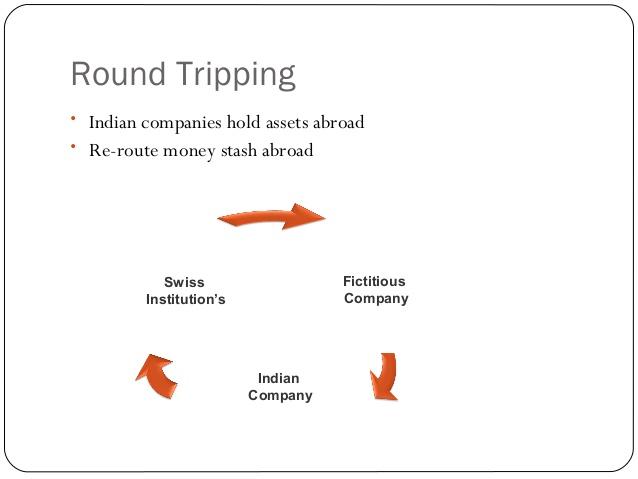
Round Tripping
In the context of black money, it leaves the country through various channels such as inflated invoices, payments to shell companies overseas, the hawala route, and so on.
After cooling its heels overseas for a while, this money returns in a freshly laundered form; thus completing a round-trip.
How does money laundering work?
- Placement of the launderer introduces his illegal profits into the financial system. This might be done by breaking up large amounts of cash into less conspicuous smaller sums that are then deposited directly into a bank account.
- Layering a series of conversions or movements of the funds to distance them from their source. – use of widely scattered accounts for laundering is especially prevalent in those jurisdictions that do not co-operate in anti-money laundering investigations.
- Integration – in which the funds re-enter the legitimate economy. The launderer might choose to invest the funds into real estate, luxury assets, or business ventures.

Source-Google
The vulnerability of India (International Narcotics Control Strategy Report)
- India’s emerging status as a regional financial center
- Weak laws & willful defaulters
- its large system of informal cross-border money flows (Hawala)
- its widely perceived tax avoidance problems
- Poor GAAR Implementation
- Unholy nexus
- narcotics trafficking
- illegal trade in endangered wildlife, trade-in illegal gems (particularly diamonds), smuggling,
- trafficking in persons,
- India’s geographical location between the heroin-producing countries of the Golden Triangle and Golden Crescent.
Reasons for Persisting ML
- Absence of deals for sharing tax information with other countries.
- Corporate Secrecy Laws – as the corporate law of certain countries enables launderers to hide behind shell companies.
- Tight Bank Secrecy Laws.
- A high degree of Economic Dependence on the Financial Services Sector.
- A Geographical Location that Facilitates Business Travel to and from rich neighbors.
Consequences/Impacts
- Naxalism, Extremism, Terrorism, Communalism
- Weakens Political System (Unfair elections)
- Undermining of the legitimate private sector
- Undermining of the integrity of financial markets
- Loss of control of economic policy
- Economic distortion and instability
- Loss of revenue: decreases the tax funds
- Security threats to privatization efforts
- The reputation risk to the countries
Institutional Measures were taken by the Government
- The financial intelligence unit-India (FIU-India) is the nodal agency in India for managing the anti-MONEY LAUNDERING ecosystem. It helps in co-coordinating and strengthening efforts to reduce MONEY LAUNDERING and related crimes in India.
- Prevention of MONEY LAUNDERING Act, 2002 has been the core framework for combating it. and subsequent amendments to strengthen the act Prevention of MONEY LAUNDERING (Amendment) Bill, 2012.
- The Enforcement directorate carries out investigations. The ED is also empowered to attach property entities involved in money laundering.
- A special cell called Combating Financing of Terrorism (CFT) Cell was created in the Internal Security Division of MHA in 2011 to coordinate with Central Intelligence Enforcement Agencies and the State Law Enforcement Agencies to develop an integrated approach to tackle the problem of terror funding.
Legal Measures were taken by Government
- The Smugglers and Foreign Exchange Manipulators (Forfeiture of Property) Act, 1976.
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985.
- Benami Transactions Prohibition Act
- COFEPOSA or the Conservation of Foreign Exchange and Prevention of Smuggling Activities Act,1974 .
- Demonetization
- UAPA, 1967
- Foreign income & assets discloser Act
- Prevention of Money-laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) through Finance Act 2018.
Global Efforts
Global steps to counter the problem:
- G 20: Information Exchange Agreements
- DTAA Amended (Mauritius, Cyprus, Singapore)
- UN Office on Drugs & Crime
- FATCA by the USA
- Revised BITs
- GAAR implementation
- SEBI Stringent rules regarding P-Notes
- CCIT
- United Nations Convention against illicit traffic in Narcotic Drugs and psychotropic substances: India’s urgent need to control drug trafficking reflects a growing awareness within the international community that drug trafficking and money laundering must be suppressed. The United has played an integral role in the global community’s fight against illicit drug trafficking and money laundering.
- Financial Action Taskforce on money laundering: Intergovernmental groups have also taken action against the rising levels of global money laundering. The task force was created by G-7 countries to curb the occurrence of money laundering.
- Basle Committee Minimum standards
Money laundering for UPSC Questions-
- 2013 – Money laundering poses a serious threat to the country’s economic sovereignty. What is its significance for India and what steps are required to be taken to control this menace?
- 2018 – India’s proximity to two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering, and human trafficking. What countermeasures should be taken to prevent the same?