INDEX
- What is Cyber Security?
- Status of India
- Challenges
- International Convention on Cybercrime
- Government Initiatives
- Way Forward
UPSC Questions
- Cyberspace and Internet: Blessing or curse to the human civilization in the long run 2016.
- Discuss the potential threats of Cyberattack and the security framework to prevent it. 2017
- Considering the threats cyberspace poses for the country, India needs a “Digital Armed Force” to prevent crimes. Critically evaluate the National Cyber Security Policy, 2013 outlining the challenges perceived in its effective implementation. (2015)
- Cyberwarfare is considered by some defense analysts to be a larger threat than even Al Qaeda or terrorism. What do you understand by Cyberwarfare? Outline the cyber threats which India is vulnerable to and bring out the state of the country’s preparedness to deal with the same. 2013
What is Cyber security?
A set of activities and other measures, technical and non-technical, to protect computers, computer networks, related hardware and software, and the information they contain from all threats.
Cyber Security Threats
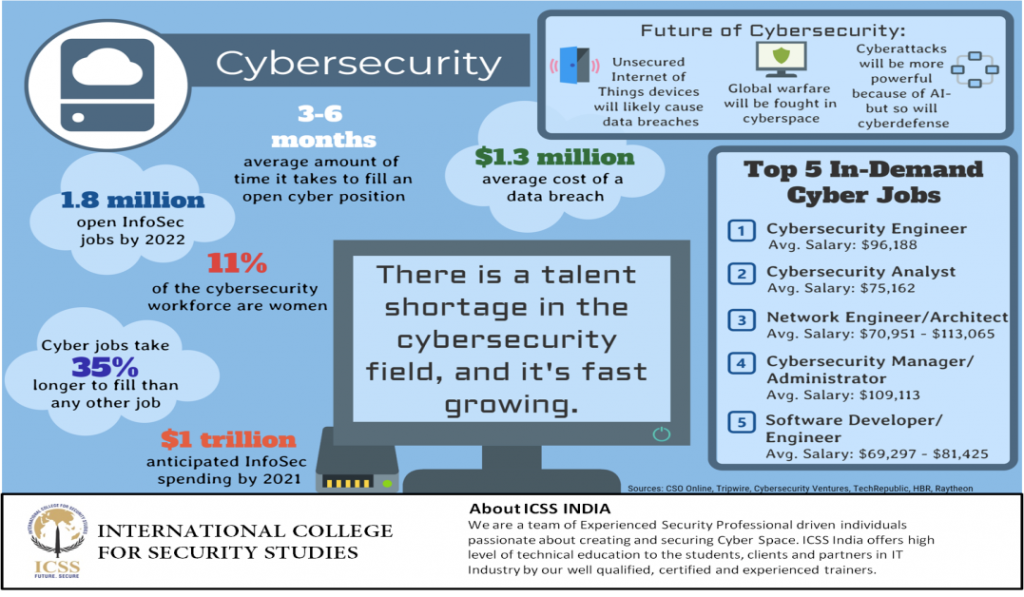
Cyber Security – Need
Vulnerability of India
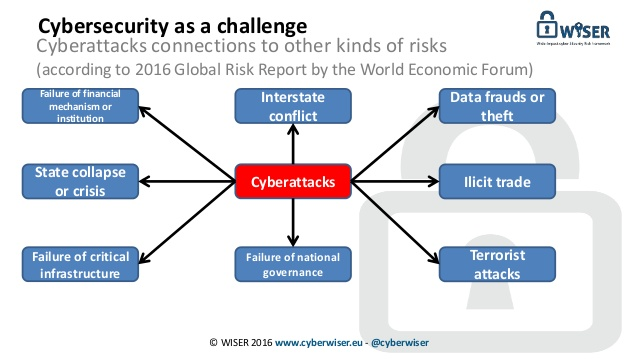
- India is vulnerable to digital intrusions such as cyber-espionage, cybercrime, digital disruption, Distributed Denial of Service.
- Increase in cases related to cybercrime by 70% in 2014 compared to 2013.
- The growing threat from online radicalization.
- Cyberwarfare has emerged as a top threat to national security with India’s systems subjected to sophisticated cyber attacks .
- Critical infrastructure: Attackers can gain control of vital systems such as nuclear plants, railways, transportation or hospitals.
Status of India

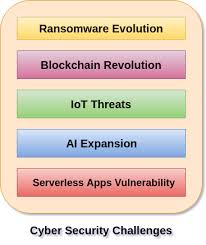
Challenges
- Ransomware attacks and demanding money are increasing. E.g: Wannacry, Petya.
- Cyberspace for spreading terrorism e.g. ISIS used cyberspace to get disillusion the people.
- Cyber theft, data hack, money theft are increasing,
- Privacy issues data sharing by renowned companies like Facebook, Google etc.
- Internet of things is often not built with security.
- Low-cost phones in developing county like India are often prone cyber attacks.
- New technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning also face new challenges for cybersecurity.
- Lack of global conventions: Budapest convention is the only global convention.
- Low digital literacy in poor and developing countries.
- Lack of cybersecurity staff
- Cyberwarfare- Countries are using cyberspace to initiate virtual war E.g: Russia on Ukraine.
Cyber security
Government Initiatives
- National Cyber Security Policy, 2013- aimed at building secure and resilient cyberspace for citizens, businesses and the Government.
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)- National nodal agency to coordinate matters related to cyber security incidents in the country.
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)- to enhance the protection and resilience of Nation‘s critical information infrastructure.
- PPP in cooperation and collaboration for responding to cyber security incidents.
- Information Security Education and Awareness (ISEA) Project- objective of capacity building in the area of Information Security, training of Government personnel and creation of mass Information Security awareness.
- Cyber forensics training labs in all north eastern states and training of police personnel and CBI in these labs
- Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP)– for countering cyber threats and cyber terrorism.
- National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC)- to generate necessary situational awareness of existing and potential cyber security threats and enable timely information sharing for proactive, preventive and protective actions by individual entities.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra- provides for detection of malicious programs and free tools to remove the same.

Way Forward – Gulshan Rai Committee and Standing Committee on Information Technology-
- Establishing a National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre to tackle cyber-attacks.
- Single centralised body to have better regulation.
- Government organisations should obtain ISO certification for best practices related to information security.
- Develop capable human resources to build security experts and skilled IT personnel.
- Allocating funds for R&D for the development of key strategic technologies.
- Internet servers for critical sectors should be hosted within the country .
- Periodic revision of domestic laws such as IT Act, 2000 and National Cyber Security Policy, 2013 should be done to meet changing demands of the time.
Way Forward – Other suggestions
- Bleeding edge technology, that is, technology that has been released but made not available to public because it has not been reliably tested.
- Big data analytics to find possible threats.
- Air gapping critical infrastructure, it involves isolating a computer or network and preventing it from establishing an external connection.
- Offensive cyber operations.
- Emphasis on cloud computing techniques.
International Convention on Cybercrime
- Also known as Budapest Convention
- First international treaty that addresses cybercrime by harmonising national laws, improving legal authorities for investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations.
- Only multilateral convention on cyber security .
- Considered critical to economic and national security of a country.
Developing countries including India have not signed; stating that developed countries lead by the US-drafted it without consultation.
Telegram https://t.me/diademyias
Email : contact@diademy.com 011-41561002