UPSC PRELIMS+MAINS
Index
- A) Indices, Reports, Surveys, Committees and Organisations
- Asian Development Bank (ADB) (PIB)
- B) Science and Technology, Defence, Space
- Kerala on alert after bird flu in two districts (TH)
- India, Antarctica, Arctic and More (PIB)
- C) Agriculture, Geography, Environment and Biodiversity
- Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960 and Animal Welfare Board (TH)
- D) Art, Culture and History
- Jagdish Chandra Bose (PIB)
- E) International Relations
- Vietnam buys Indian rice for first time in decades (TH)
- F) Economic Developments: India and World
- Regulation S bonds and the Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank) (TH)
- G) Polity, Bills, Acts and Judgments
- Tenth Schedule of the Constitution for Defection (TH)
- H) Miscellaneous
- East Container Terminal (ECT) (TH)
A) Indices, Reports, Surveys, Committees and Organisations
-
Asian Development Bank (ADB) (PIB)
- Context: The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Government of India signed a $100 million loan to modernise and upgrade the power distribution system to enhance the quality and reliability of electricity supply in Bengaluru city in the state of Karnataka.
- Asian Development Bank was covered comprehensively in 2 Dec file.
B) Science and Technology, Defence, Space
2.Kerala on alert after bird flu in two districts (TH)
- Kerala was placed on high alert after an outbreak of bird flu was confirmed in some of the districts.
- The presence of the H5N8 subtype of the Influenza A virus was reported in ducks in many districts.
- Five of eight samples airlifted to the National Institute of High Security Animal Diseases, Bhopal, tested positive for the virus.
- Culling of ducks in the infected regions would be undertaken as per Central guidelines.
Analysis
Bird Flu
- H5N1is a type of influenza virus that causes a highly infectious, severe respiratory disease in birds called avian influenza (or “bird flu”).
- These flu viruses occur naturally among birds. Wild birds worldwide carry viruses in their intestines, but usually do not get sick from them. However, bird flu is very contagious among birds and can make some domesticated birds, including chickens and ducks, very sick and kill them.
How does avian flu spread in birds?
- Infected birds shed flu viruses in their saliva, nasal secretions, and feces (droppings). Susceptible birds become infected when they have contact with contaminated excretions or surfaces that are contaminated with excretions.
- Infected birds pass on H5N1through their saliva, nasal secretions, and feces.
- H5N8 first appeared in China in 2014.
- The strain came from the H5N1 virus which started its menace in China in 1996.
Do avian flu viruses infect humans?
- Bird flu viruses do not usually infect humans, but several cases of human infection with bird flu viruses have occurred since 1997.
- Human cases of H5N1avian influenza occur occasionally, but it is difficult to transmit the infection from person to person.
- While it can prove lethal for birds, the H5N8 strain of avian influenza has a lower likelihood of spreading to humans compared to H5N1.
Swine flu
- The pandemic influenza strain, or swine flu, that spread globally in 2009 was referred to as
- There are four major types of influenza that infect humans, known as influenza A, B, C and D.
- Influenza A and B can both cause serious infections and are the cause of what we call the flu.
- Influenza C viruses differ from influenza A and B, and only cause a mild infection, so they don’t appear in vaccines.
- Influenza viruses infect humans and many different animals.
- Influenza B viruses circulate among humans and cause seasonal epidemics.
- Influenza C viruses can infect both humans and pigs but infections are generally mild and are rarely reported.
- Influenza D viruses primarily affect cattle and are not known to infect or cause illness in people.
- Influenza type A viruses are of most significance to public health due to their potential to cause an influenza pandemic.
- Depending on the origin host, influenza A viruses can be classified as avian influenza, swine influenza, or other types of animal influenza viruses.
- Aquatic birds are the primary natural reservoir for most subtypes of influenza A viruses.
- A pandemic influenza strain is one that humans have not been previously exposed to, so people do not have immunity to it.
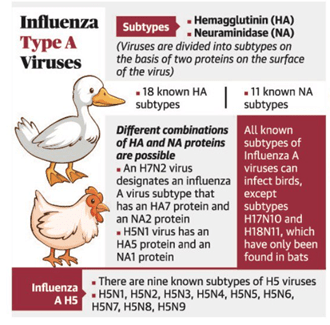
Hs and Ns
- Surface antigens (foreign proteins) haemagglutinin
(H) and neuraminidase (N) form the viral coat of the H1N1 influenza viruses.
- Viruses attach by their haemagglutinin onto receptors on the surface of cells in order to infect them, like a grappling hook.
- The neuraminidase removes these receptors from infected cells at the right time to allow newly synthesized viruses to escape and spread.
- Among influenza A viruses there are 18 different types of haemagglutinin, from H1 to H18 and 11 different types of neuraminidase, from N1 to N11. Each virus has one type of H (such as H1) and one type of N (such as N1).
- Influenza B strains do not circulate in animals, so they cannot cause a pandemic. But, like influenza A viruses, they continually change, so we will never become immune to every strain.
-
India, Antarctica, Arctic and More (PIB)
- Context: India launched the 40th scientific expedition to Antarctica.
- The Indian Antarctic expeditions began in 1981.
- The Indian Antarctic program has now credited to have built three permanent research base stations in Antarctica—named Dakshin Gangotri, Maitri, and Bharati.
- As of today, India has two operational research stations in Antarctica named Maitri and Bharati.
- The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Goa, manages the entire Indian Antarctic program.
C) Agriculture, Geography, Environment and Biodiversity
4.Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960 and Animal Welfare Board (TH)
- Context: The Supreme Court asked the Centre to “delete” its law, which allowed authorities to seize cattle on a mere suspicion that they suffered cruel treatment at the hands of their owners or were being primed for slaughter.
- As per rules framed under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960 these animals would then be lodged in ‘gaushalas’ as “case property” to await the court’s verdict.
- In short, a farmer, a livestock owner or a cattle trader loses his animals even before they were found guilty of cruelty towards them.
Analysis
Salient features of the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960
- This act provides for punishment for causing unnecessary cruelty and suffering to animals.
- This act defines animals and different forms of animals.
- This Act enshrines the provisions relating to the establishment of an animal welfare board, its constitution, powers, and functions.
- This act discusses different forms of cruelty, exceptions, and killing of a suffering animal in case any cruelty has been committed against it, so as to relieve it from further suffering.
- This act provides the guidelines relating to experimentation on animals for scientific purposes.
- This act enshrines the provisions relating to the exhibition of the performing animals, and offences committed against the performing animals.
- This Act provides for the limitation period of 3 months beyond which no prosecution shall lie for any offenses under this Act.
- According to this Act an animal refers to any living creature excluding a human being. Therefore, this definition is comprehensive and exhaustive. For animals, it refers not solely to mammals, but also includes birds, reptiles, etc.
- Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960 enshrines the provisions relating to the constitution, funding, and functioning of the animal welfare board.
Animal Welfare Board
- The Animal Welfare Board of India is a statutory advisory body under Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- It established by the Central Government purporting to provide for animal welfare and extending protection against animals from unnecessary pain or suffering.
- It was the first of its kind to be established by any Government in the world.
- It is permanently chaired by a senior official of the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF).
- Shrimati Rukmini Devi Arundale pioneered the setting up of the Board.
- The headquarters of the Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI) has been shifted from Chennai to Haryana’s Ballabhgarh for “better coordination ” between the environment ministry and the board.
Some important Functions of the Board
- To advise the Government or any local authority or another person on improvements in the design of vehicles so as to lessen the burden on draught animals.
- To impart education in relation to the humane treatment of animals.
- To advise the Government or any local authority or another person in connection with the slaughter of animals so that unnecessary pain or suffering is eliminated in the pre- slaughter stages as far as possible
- To ensure that unwanted animals are destroyed by local authorities, whenever it is necessary to do so, either instantaneously or after being rendered insensible to pain or suffering.
- To give financial assistance and other assistance to Animal Welfare Organisations functioning in any local area or to encourage the formation of Animal Welfare Organisations in any local area.
- To give financial and other assistance to animal hospitals whenever the Board think it is necessary to do so.
- The AWBI, however, does not have the right to prescribe punishments or fines for violations of the PCA Act but can pursue legal action.
- It has in the past led litigation to disallow the use of bulls in Jallikattu in Tamil Nadu.
- The Board consists of 28 Members. The term of office of Members is for a period of 3 years.
- The Board grants recognition to the newly started Animal Welfare Organisations (AWOs).
Funds of the Board shall consist of:
- Governmental grants allocated to it time and again;
- Contributions, donations, gifts, subscriptions, etc. made to the Board by any individual or local authority.
- Note: Nothing in this Act shall affect the experimentation (including operations) on animals for the purpose of.
- combating any disease or
- advancement through the new discovery of physiological knowledge;
- or knowledge which will be useful for decreasing the mortality rate; or Suffering alleviation; of either human beings, animals, or plants.
D) Art, Culture and History
5.Jagdish Chandra Bose (PIB)
- Context: Many times, research might not fulfil its immediate goal but the same research can become path-breaking in some other sector.
- The Prime Minister illustrated this point by the example of Jagdish Chandra Bose whose microwave theory could not be taken forward commercially but today, the entire radio communication system is based on that.
Analysis
Sir J C Bose
- Inspired by lofty nationalistic ideals, Bose Institute was set up in 1917 in Calcutta by Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose (1858 – 1937), the founder of modern science in the Indian subcontinent.
- It is Asia’s first modern research centre devoted to interdisciplinary research.
- On this occasion, he delivered his famous address “The voice of life” and dedicated the institute to the service of the nation.
- Bose’s Galena detector was the first semiconductor device and a photovoltaic cell.
- He also designed the earliest waveguide and Horn Antenna, an integral part of present-day microwave engineering and astronomy.
- Sir J.C. Bose demonstrated his wireless millimeter wave (microwave) experiments at the Royal Institution, London in January 1897.
- This predates the wireless experiments at Salisbury Plain in May 1897 by Marconi, to whom the Nobel prize was however awarded.
- Most notably, in 1895, he was the first to demonstrate the wireless transmission and reception of electromagnetic waves at Presidency College (now Presidency University), Kolkata.
- Indeed, Bose was a pioneer of multimedia communication in every way.
- He was the first Asian to be awarded a US patent in 1904.
- Bose and the legendary mathematician Ramanujam were also the first Asian fellows of the Royal Society, London as well as those of Vienna and Finland.
- Bose has been recognized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers(IEEE) as a father of radio and wireless communication.
- His work was also commemorated by IEEE as the oldest “milestone achievement” from Asia.
- He was a member from Asia on the International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation of the League of Nations along with Einstein, Curie and Millikan.
- Besides being a physicist par excellence, another remarkable contribution of J. C. Bose was that he was the first in the world to initiate interdisciplinary research by probing plants from the vantage point of physics – an integrated biophysical view of life that is in vogue.
- His studies on coherer led to the discovery of the common nature of the electric response to external stimuli by both living and inanimate objects.
- Many of these experiments were possible because of his design and fabrication of novel instruments like crescograph, photosynthetic bubbler, sonograph etc.
- Two of his famous books are “Response in the Living and Non-Living” (1902) and “The Nervous Mechanism of Plants” (1926).
- The latter book was dedicated to his friend the great poet and Asia’s first Nobel laureate, Rabindranath Tagore. Tagore’s great admiration of Bose reflects in his poems.
- He is also considered the father of Bengali science fiction.
- He was neither awarded Nobel Prize nor Bharat Ratan.
E) International Relations
6.Vietnam buys Indian rice for first time in decades (TH)
- Context: Vietnam, the world’s third-biggest exporter of rice, has started buying the grain from rival India for the first time in decades after local prices jumped to their highest in nine years amid limited domestic supplies.
Analysis
- The purchases underscore tightening supplies in Asia, which could lift rice prices in 2021 and even force traditional buyers of rice from Thailand and Vietnam to switch to India — the world’s biggest exporter of the grain.
- Indian prices are very attractive. The huge price difference is making exports possible. Vietnam’s 5% broken rice is offered at about $500-$505 per tonne, compared to Indian prices of $381-$387.
- Dwindling supplies and continued Philippine buying lifted Vietnamese rice export prices to a fresh nine-year high.
- Below are the countries that exported the highest dollar value worth of rice during 2019.
- India: (32.5% of total rice exports)
- Thailand: (19.2%)
- United States: (8.6%)
- Vietnam: (6.6%)
- Pakistan: (5.6%)
- China: (4.8%)
- Italy: (2.9%)
- Myanmar (Burma): (2.6%)
- Cambodia: (2%)
- Uruguay: (1.7%)
F) Economic Developments: India and World
7.Regulation S bonds and the Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank) (TH)
- Context: The Exim Bank is in the dollar money market with a seven-year bond issue, selling Reg S bonds worth at least $1 billion.
- Regulation S bonds are issued by foreign issuers in the U.S. debt market and are denominated in U.S. dollars, but resident American citizens cannot subscribe to them.
Analysis
- Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank) is a specialized financial institution, wholly owned by the Government of India, set up in 1982, for financing, facilitating and promoting foreign trade of India.
- EXIM Bank extends Lines of Credit (LOCs) to overseas financial institutions, regional development banks, sovereign governments and other entities overseas, to enable buyers in those countries to import developmental and infrastructure projects, equipment, goods and services from India, on deferred credit terms.
- EXIM Bank has laid strong emphasis on enhancing project exports, the funding options for which have been enhanced with the introduction of the Buyer’s Credit-National Export Insurance Account (BC-NEIA) program.
- The Bank facilitates two-way technology transfer by financing import of technology into India, and investment abroad by Indian companies for setting up joint ventures, subsidiaries or undertaking overseas acquisitions.
- The Bank provides assistance in helping Indian firms in their globalization efforts by locating overseas distributor(s)/ buyer (s)/ partner (s) for their products and services.
- Exim Bank also lays special emphasis on enhancing export capabilities and international competitiveness of Indian companies through its various Advisory Services.
G) Polity, Bills, Acts and Judgments
8.Tenth Schedule of the Constitution for Defection (TH)
- Context: Congress through its advocates complained about the delay of over a year and a half by the State Assembly Speaker to decide the disqualification petitions filed against 10 Congress MLAs who defected to the BJP in July 2019. The Supreme Court Bench scheduled the case for hearing in the second week of February.
H) Miscellaneous
9.East Container Terminal (ECT) (TH)
- Sri Lanka, Japan and India signed an agreement to jointly develop the East Container Terminal at the Colombo Port.
- The East Container Terminal (ECT) is located some 3 km away from the China-backed international financial city, known popularly as “port city”, being built on reclaimed land on Colombo’s seafront.